Trumpet Introduction
Share

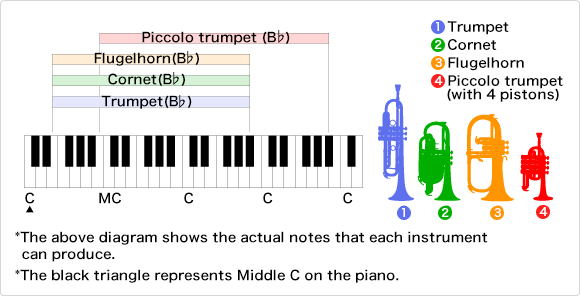
Trumpet
The trumpet is characterized by its striking, triumphal sound and by the fact that it boasts the highest register of all the brass instruments. It does splendid work, single-handedly giving expression to heroism and jubilation.

Trumpet
Sound is produced by buzzing the lips!
The trumpeter produces sound from the trumpet by buzzing his lips. That said, it is in fact the metallic mouthpiece that produces the sound.
The trumpet or cornet is the smallest and highest member of the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by buzzing the lips into a mouthpiece.
The trumpet is stored in the case in just two pieces, the body and the mouthpiece.
The trumpet is a very versatile and widely used instrument. Trumpets are always needed in bands, symphony orchestras, jazz groups and small instrumental groups. It is very common for the trumpet to perform a large number of solos and melodic lines in all of these groups. The trumpet also works well as a solo instrument.
The origins of the Trumpet
The birth of the trumpet
The forerunners of the trumpet were made out of various materials and came from various locations
The origins of the trumpet can be traced back several thousand years. However, since the primitive trumpets were rudimentary wind instruments that the player sounded simply by moving his lips, they cannot clearly be distinguished from the forerunners of the horn, on which sound is produced in the same way.
Trumpets of old were made out of various materials, including wood, bamboo, bark, clay, human bone, and metal. Found on every continent, they are thought to have been used in religious ceremonies and sorcery.
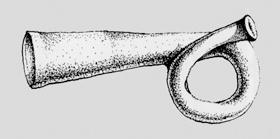
Ancient trumpet made of clay, found in Peru.
The trumpet before modern times
In the ancient Greek and Roman eras, trumpets were used for marching in wartime, for which they were admirably suited. Subsequently, almost all European royalty had trumpet bands that played military music.
It was in the seventeenth century that the trumpet came to be used purely in musical ensembles. At that time, however, this was still the so-called natural trumpet, which can only produce natural harmonics, so the trumpet was not yet a fully functional instrument.

A trumpet depicted in the Triumphal Arch of Titus. Jerusalem, second century
The origins of the Trumpet
The invention of the valve
Was the trumpet unable to play scales in olden times?
Early trumpets had a very simple shape, with just a flared bell at the end. The trumpeter could produce a number of different notes by varying his lip movement and the speed of his breath. These notes are known as harmonics and are written on a score as follows:

An early trumpet
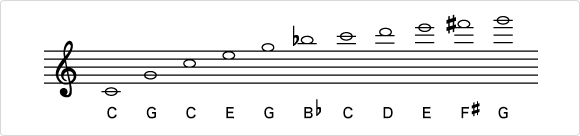
An example of harmonics on the trumpet
Do the valves change the length of the tube?
Melodies were played on early trumpets using the run of high-harmonic notes, as shown on the right of the score above. When a trumpeter needed to play songs in different keys, such as C major and G major, he would keep a C major trumpet and a G major trumpet to hand. Looking after all these instruments and carrying them around was very troublesome, however. Accordingly, in around 1810 the valve was invented as a means for easily changing the length of the tube.
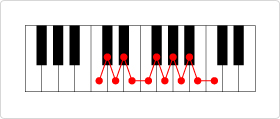
A chromatic scale is a scale in which one octave is divided into 12 semitones.
A valve is a device that changes the path taken by the trumpeter's breath. A second tube was added in the middle of the instrument's tube and a valve was attached at the point where they joined. The valve controlled which tube the trumpeter's breath would pass through. It was now easy to change the length of the tube, enabling chromatic scales to be played on the trumpet.
The origins of the Trumpe
The relatives of the trumpet
Cornet and flugelhorn
The cornet and the flugelhorn are also relatives of the trumpet. Compared to the trumpet and the cornet, however, both of which have tubes that are almost cylindrical along their entire length, the flugelhorn has a pronounced conical shape. Since a conical tube produces a mellower sound than a cylindrical tube, the instrument creates a completely different impression. Try comparing the different instruments by listening to the sounds that they produce.
| Instrument | Appearance | Listen to a sample |
|---|---|---|
| Trumpet |  |
|
| Cornet |  |
|
| Flugelhorn |  |